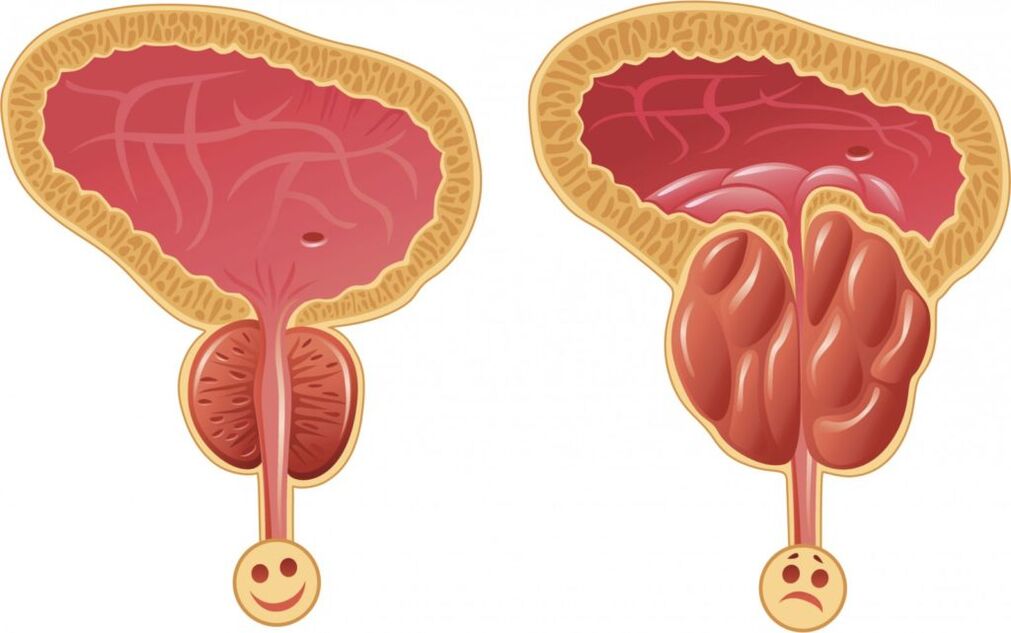
Approximately one third of men of active reproductive age - ages 20 to 40 - suffer from chronic prostatitis. Due to the disease, the quality of life of many patients is markedly reduced. Chronic prostatitis is difficult to treat, but it is possible to improve well-being, restore impaired functions and get rid of painful symptoms for a long time. The main thing is to choose the right treatment regimen. Obviously, this is the doctor's task, but in any case, it is useful to know which drugs can be used in the treatment. Let's talk about what drugs for prostatitis exist and how they work.
Prostatitis drug groups
Any disease - and prostatitis is no exception - has a cause, a mechanism for the development of the pathological process and clinical manifestations. Accordingly, the directions of treatment also differ.
The question may arise: why is it impossible to limit ourselves to etiotropic treatment, because after eliminating the cause, the development of the disease must stop and the symptoms will disappear? In the case of chronic diseases, including prostatitis, not everything is so simple. First, it is not always possible to find and eliminate the cause. Second, when the pathological mechanism is already running, it sustains itself, and even the elimination of the etiological factor does not guarantee recovery. Therefore, a universal cure for prostatitis has not yet been developed: today all links in therapy are important.
etiotropic drugs
The etiology of chronic prostatitis is not well understood. On the one hand, infection is considered to be the cause of the development of the inflammatory process. No microbes are found in the tissues of a healthy prostate. On the other hand, the proportion of bacterial prostatitis is only about 10% in the general structure of incidence, the remaining 90% of cases are abacterial forms. Infection probably plays a role only at an early stage in the development of the disease, being the trigger of the pathological process in the prostate. In the future, the importance of microbial flora diminishes and pathological changes in prostate tissues (congestion, impaired microcirculation, autoimmune mechanisms and so on) become more important factors. What drugs for prostatitis are used?
Etiotropic therapy of bacterial prostatitis involves the appointment of antibiotics. With your selection, too, not everything is as simple as it seems. First, the spectrum of microorganisms is changing: if until recently E. coli was prevalent among the causative agents of chronic prostatitis, now chlamydia, mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, gardnerella, trichomonas are increasingly found. They are not sensitive to previously used antibiotics. Second, the resistance of microbes to the effects of antibacterial agents is growing. Therefore, etiotropic drugs for the treatment of prostatitis should be prescribed only after determining the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Effective antibacterial drugs against prostatitis are consideredfluoroquinolones. They penetrate well into prostate tissues and form concentrations high enough to destroy microbes. Another advantage of fluoroquinolones is a broad spectrum of action: many types of pathogenic bacteria are sensitive to them. This group of drugs against prostatitis includes active substances such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin and others.
When chlamydia and other intracellular microorganisms are detected,macrolidesandtetracyclines. They are active against specific flora, but have a bad effect on pathogens typical of chronic prostatitis - Escherichia coli, staphylococci. The advantage of macrolides is their low toxicity.
Pathogen therapy preparations
Against the background of chronic inflammation in the tissues of the prostate, a complex of changes occurs. There is a stagnation of secretion, the venous flow worsens, the trophism of the gland is disturbed, fibrosis gradually develops (replacement of healthy connective tissue), immunity suffers. These interrelated pathological changes support the inflammatory process and reduce the effectiveness of etiotropic therapy. Restoring the structure and functions of the gland with the help of pathogenic therapy helps to break the vicious circle. As many factors are involved in the pathogenesis of chronic prostatitis, the drugs in this group are diverse.
- Immunomodulators. In a chronic inflammatory process, the work of all parts of the immune system is disrupted. Immunomodulators regulate defense mechanisms, helping to deal with inflammation and infection. This is a large group of drugs with different mechanisms of action.
- antioxidants. One of the pathological mechanisms that accompany inflammation is oxidative stress. Prostate cells are damaged by free radicals, which are formed in large quantities due to a sharp increase in the leukocyte content in the prostate secretion. Oxidative stress exacerbates and maintains the inflammatory response. To stop this process, antioxidants are prescribed for chronic prostatitis: zinc, selenium, copper preparations, vitamins A, C, E, folic acid, L-carnitine, glutathione, resveratrol and others.
- Enzyme preparations. As a result of chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, lack of blood supply, healthy glandular tissue is replaced by connective tissue. Enzyme preparations (mainly based on hyaluronidase) delay the development of fibrosis.
Observation
Among the drugs used for prostatitis, peptide bioregulators obtained from the prostate of animals deserve special attention. They have a selective effect on the prostate, in particular, they improve blood flow and restore microcirculation. Due to this, swelling decreases, the risk of blood clots decreases, pain decreases, urination normalizes, and prostate functions are restored. In some cases, it is possible to use these drugs for the prevention of prostatitis.
symptomatic drugs
One of the main goals of treating chronic prostatitis is to save patients from the painful manifestations of the disease. Symptomatic agents do not affect the course of the inflammatory process, but relieve the condition of patients. So what helps with prostatitis?
- alpha blockersblock nerve impulses from receptors located in the smooth muscles of the prostate, urethra, bladder. As a result, the spasm stops, the pain disappears, urination normalizes. The action does not occur immediately, but after two weeks of starting treatment.
- antispasmodicsprescribed for the same purpose as alpha-blockers. They help to relax smooth muscles. Due to the removal of the spasm, the pain subsides, the flow of urine is restored.
- InesUsed to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. These drugs work quickly but cannot be used for long periods because of the risk of side effects.
The drug in the form of suppositories helps to restore the functions of the prostate, helping to relieve pain and improve the process of urination.
How to choose a drug for the treatment of prostatitis
The urologist selects the therapeutic regimen and drugs for the treatment of prostatitis based on the diagnostic results and analysis of the patient's complaints. The therapy of this disease must be comprehensive: this is the only way to obtain a stable and lasting effect. If the tests reveal an infection, the doctor will definitely prescribe antibiotics according to the type of pathogen. In other cases, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is used. The latter is selected based on the predominant complaints. For example, if the patient is concerned about pain, NSAIDs are prescribed. For problems with urination, alpha-blockers are used.
Drugs used for prostatitis differ not only in the composition and mechanism of therapeutic action, but also in the form of release. The main ones are tablets, capsules and rectal suppositories. Medicines in the form of injections are used less often.

Pills and capsules are convenient to take. However, suppositories, in the first place, act more quickly: through the wall of the rectum, which is in contact with the prostate, the active substance is delivered via the lymphogenic route immediately to the site of inflammation. Secondly, drugs in the form of suppositories have greater bioavailability: unlike tablets, they are not metabolized in the liver and the concentration of active ingredients does not decrease. Finally, suppositories are safer in terms of side effects: in particular, they have practically no negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
In modern treatment regimens for chronic prostatitis, attention is paid to all components of therapy: etiotropic, pathogenic, and symptomatic. Medications should be selected by the physician, focusing on test results and patient complaints. An integrated approach to treatment and the right choice of drugs help to restore impaired functions and forget about the symptoms of prostatitis for a long time.
Suppositories for Prostatitis
One of the drugs often prescribed by urologists for the treatment of chronic prostatitis is drugs in the form of suppositories. This tool has been used in clinical practice for over 30 years.
The active ingredient in the suppositories is bovine prostate extract. It contains a complex of peptides that have a regulatory effect on prostate cells. The drug helps improve microcirculation and venous flow, thereby reducing inflammation and swelling and reducing pain.
Indications for use - chronic abacterial prostatitis, conditions before and after prostate surgery, benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Suppositories are highly bioavailable. Low molecular weight peptides easily penetrate biological barriers and are delivered to the focus of inflammation. The high degree of purification minimizes the risk of allergic reactions and other undesirable reactions.
Suppositories with bovine prostate extract are compatible with antibiotics and other drugs used in the complex therapy of chronic prostatitis. The means is applied by a short course (10 days). It is, however, affordable.